Chapter 21
Camouflage
In a survival situation, especially in a hostile environment, you may
find it necessary to camouflage yourself, your equipment, and your movement.
Effective camouflage may mean the difference between survival and capture by
the enemy. Camouflage and movement techniques, such as stalking, will also
help you get animals or game for food using primitive weapons and skills.
PERSONAL CAMOUFLAGE
In a survival situation, especially in a hostile environment, you may find it necessary to camouflage yourself, your equipment, and your movement. Effective camouflage may mean the difference between survival and capture by the enemy. Camouflage and movement techniques, such as stalking, will also help you get animals or game for food using primitive weapons and skills.
21-1. When camouflaging yourself, consider that certain shapes are particular to humans. The enemy will look for these shapes. The shape of a hat, helmet, or black boots can give you away. Even animals know and run from the shape of a human silhouette. Break up your outline by placing small amounts of vegetation from the surrounding area in your uniform, equipment, and headgear. Try to reduce any shine from skin or equipment. Blend in with the surrounding colors and simulate the texture of your surroundings.
SHAPE AND OUTLINE
21-2. Change the outline of weapons and equipment by tying vegetation or strips of cloth onto them. Make sure the added camouflage does not hinder the equipment's operation. When hiding, cover yourself and your equipment with leaves, grass, or other local debris. Conceal any signaling devices you have prepared, but keep them ready for use.
COLOR AND TEXTURE
21-3. Each area of the world and each climatic condition (arctic/winter, temperate/jungle, or swamp/desert) has color patterns and textures that are natural for that area. While color is self-explanatory, texture defines the surface characteristics of something when looking at it. For example, surface textures may be smooth, rough, rocky, leafy, or many other possible combinations. Use color and texture together to camouflage yourself effectively. It makes little sense to cover yourself with dead, brown vegetation in the middle of a large grassy field. Similarly, it would be useless to camouflage yourself with green grass in the middle of a desert or rocky area.
21-4. To hide and camouflage movement in any specific area of the world, you must take on the color and texture of the immediate surroundings. Use natural or man-made materials to camouflage yourself. A few examples include camouflage paint, charcoal from burned paper or wood, mud, grass, leaves, strips of cloth or burlap, pine boughs, and camouflaged uniforms.
21-5. Cover all areas of exposed skin, including face, hands, neck, and ears. Use camouflage paint, charcoal, or mud to camouflage yourself. Cover areas that stick out more and catch more light (forehead, nose, cheekbones, chin, and ears) with a darker color. Cover other areas, particularly recessed or shaded areas (around the eyes and under the chin), with lighter colors. Be sure to use an irregular pattern. Attach vegetation from the area or strips of cloth of the proper color to clothing and equipment. If you use vegetation, replace it as it wilts. As you move through an area, be alert to the color changes and modify your camouflage colors as necessary.
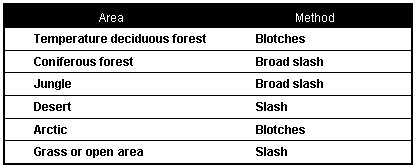
21-6. Figure 21-1 gives a general idea of how to apply camouflage for various areas and climates. Use appropriate colors for your surroundings. The blotches or slashes will help to simulate texture.
Figure 21-1. Camouflage Methods for Specific Areas
SHINE
21-7. As skin gets oily, it becomes shiny. Equipment with worn-off paint is also shiny. Even painted objects, if smooth, may shine. Glass objects such as mirrors, glasses, binoculars, and telescopes shine. You must cover these glass objects when not in use. Anything that shines will automatically attract attention and will give away your location.
21-8. Whenever possible, wash oily skin and reapply camouflage. Skin oil will wash off camouflage, so reapply it frequently. If you must wear glasses, camouflage them by applying a thin layer of dust to the outside of the lenses. This layer of dust will reduce the reflection of light. Cover shiny spots on equipment by painting, covering with mud, or wrapping with cloth or tape. Pay particular attention to covering boot eyelets, buckles on equipment, watches and jewelry, zippers, and uniform insignia. Carry a signal mirror in its designed pouch or in a pocket with the mirror portion facing your body.
SHADOW
21-9. When hiding or traveling, stay in the deepest part of the shadows. The outer edges of the shadows are lighter and the deeper parts are darker. Remember, if you are in an area where there is plenty of vegetation, keep as much vegetation between you and a potential enemy as possible. This action will make it very hard for the enemy to see you as the vegetation will partially mask you from his view. Forcing an enemy to look through many layers of masking vegetation will fatigue his eyes very quickly.
21-10. When traveling, especially in built-up areas at night, be aware of where you cast your shadow. It may extend out around the corner of a building and give away your position. Also, if you are in a dark shadow and there is a light source to one side, an enemy on the other side can see your silhouette against the light.
MOVEMENT
21-11. Movement, especially fast movement, attracts attention. If possible, avoid movement in the presence of an enemy. If capture appears imminent in your present location and you must move, move away slowly, making as little noise as possible. By moving slowly in a survival situation, you decrease the chance of detection and conserve energy that you may need for long-term survival or long-distance evasion.
21-12. When moving past obstacles, avoid going over them. If you must climb over an obstacle, keep your body level with its top to avoid silhouetting yourself. Do not silhouette yourself against the skyline when crossing hills or ridges. When you are moving, you will have difficulty detecting the movement of others. Stop frequently, listen, and look around slowly to detect signs of hostile movement.
NOISE
21-13. Noise attracts attention, especially if there is a sequence of loud noises such as several snapping twigs. If possible, avoid making any noise. Slow your pace as much as necessary to avoid making noise when moving around or away from possible threats.
21-14. Use background noises to cover the noise of your movement. Sounds of aircraft, trucks, generators, strong winds, and people talking will cover some or all the sounds produced by your movement. Rain will mask a lot of movement noise, but it also reduces your ability to detect potential enemy noise.
SCENT
21-15. Whether hunting animals or avoiding the enemy, it is always wise to camouflage the scent associated with humans. Start by washing yourself and your clothes without using soap. This washing method removes soap and body odors. Avoiding strong smelling foods, such as garlic, helps reduce body odors. Do not use tobacco products, candy, gum, or cosmetics.
21-16. You can use aromatic herbs or plants to wash yourself and your clothing, to rub on your body and clothing, or to chew on to camouflage your breath. Pine needles, mint, or any similar aromatic plant will help camouflage your scent from both animals and humans. Standing in smoke from a fire can help mask your scent from animals. While animals are afraid of fresh smoke from a fire, older smoke scents are normal smells after forest fires and do not scare them.
21-17. While traveling, use your sense of smell to help you find or avoid humans. Pay attention to smells associated with humans, such as fire, cigarettes, gasoline, oil, soap, and food. Such smells may alert you to their presence long before you can see or hear them, depending on wind speed and direction. Note the wind's direction and, when possible, approach from or skirt around on the downwind side when nearing humans or animals.
previous | next
All text and images from the U.S. Army Field Manual 3-05.70: Survival.
Appearance of the materials from the U.S. Army Field Manual here does not constitute or represent endorsement by probablyhelpful.com.
ProbablyHelpful.com is not responsible for inaccurate or outdated information provided by the U.S. Army Field Manual 3-05.70.